Supply chain management (SCM) is the management of a network of interconnected
businesses involved in the ultimate provision of product and service packages required
by end customers. Supply Chain Management spans all movement and storage of raw
materials, work-in-process inventory, and finished goods from point-of-origin to pointof-consumption.
To compete successfully in today’s market, the companies must have effective and
efficient supply chain network.
Due to globalization and expanding of multinational companies the supply chain network
has become crucial for the success of the Organizations. Technological changes had
brought the cost factor for information flow quite low thus increasing the flow of
information and coordination among the members of the supply chain network.
Supply chain management is the backbone of business in global and competitive world
market. Supply chains are increasingly becoming more complex and dynamic. The success
of the business often depends on the success of your supply chain. A leaner supply chains
enabling through process and IT related interventions in planning, execution and
collaboration are indeed the need of modern retail companies.
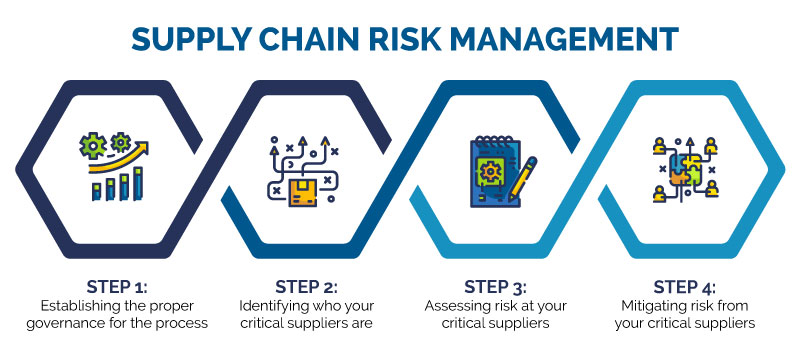
Designing of Supply Chain
The following activities are considered for designing of Supply chain network:
Strategic
1) Strategic network optimization. It includes the number, location and size of
warehousing, distribution centers and facilities.
2) Creating reliable partnership with suppliers and distributors. Right and useful
exchange of information and feedback system.
3) Product life cycle management.
4) Modern Technology for designing and executing supply chain operations.
5) Decision regarding outsourcing or manufacture, and selection of source of supply.
6) Ensuring supply strategy in align with organizational business strategy.
Tactical
1) Purchasing and source of supply selection.
2) Production planning and scheduling, decision to outsource or in house
manufacturing.
3) Decision in regard to Inventory and warehousing facilities.
4) Transportation strategy.
5) Meeting the quality standard and services of competitors by implementation of
best practices.
6) Scheduling of Payments.
7) Keeping customer demand in mind.
8) Innovative marketing techniques and new launches.
Operational
1) Production and distribution schedules.
2) Forecasting of demand and coordination with suppliers and distributors.
3) Sourcing and planning of material.
4) Inbound operations, including transportation from suppliers and receiving
inventory.
5) Production operations, inventory consumed and finished product.
6) Transportation and warehousing management.
7) Ordering at right time and proper accounting.
8) Inventory control.
9) Quality control system.
Supply chain management is getting the right things to the right places at the right
times, for profit. New information and communications technologies have
revolutionized today’s supply chains making them extraordinary better, faster and
cheaper. For example, the Cigarette supply chain involves a process from buying
tobacco leaf to turning into smoke by customers. Procurement through farmers or
government cooperatives or auction, proper storing, processing and transportation
activities form the critical process of the system